Nestled in the verdant Andean peaks of Peru, the mysterious city of Machu Picchu, a testament to the prowess of the Inca civilization, never fails to captivate explorers, historians, and casual travelers alike. This enigmatic wonder, enveloped by the ethereal mists, is a standing reminder of a civilization at its zenith before it suddenly disappeared. Machu Picchu, a UNESCO World Heritage site since 1983, holds mysteries as dense as the clouds that shroud it. As you embark on this journey, you will explore the tales of its construction, the secrets of its architecture, the riddles surrounding its purpose, and the enigmas of its sudden abandonment.
The Forgotten City Of The Incas
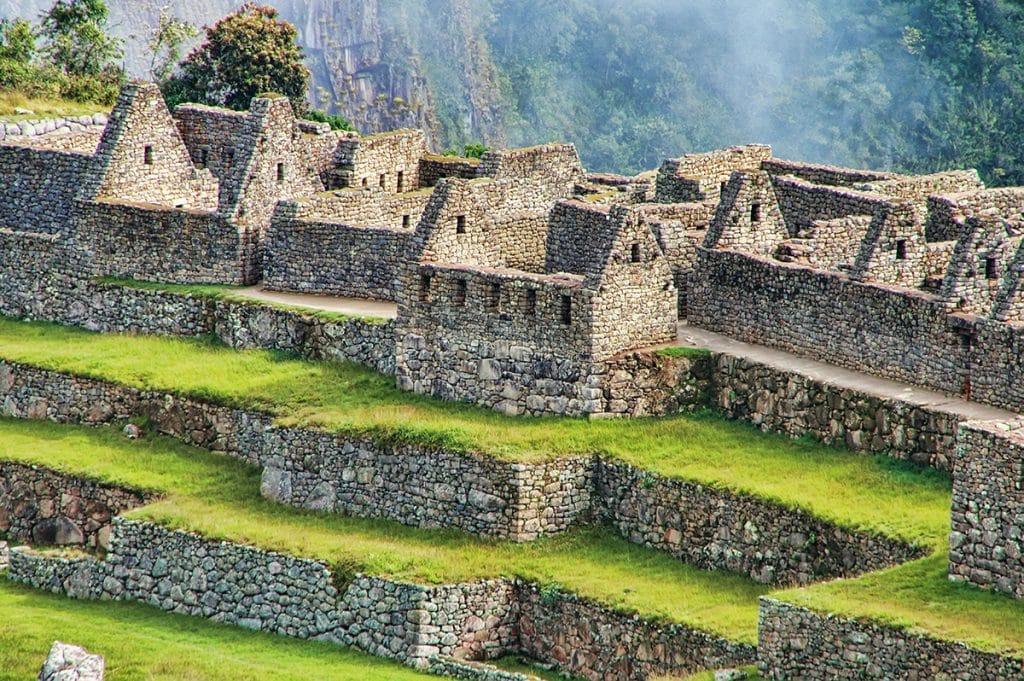

Traditionally known as the “Lost City of the Incas”, Machu Picchu’s real Incan name remains unknown. The moniker’ Machu Picchu’, simply meaning ‘Old Peak’ in the Quechua language, was attributed to it due to its location. As for the people who built this city, the Incas were an ingenious society whose architectural prowess is displayed in this city’s remains.
Over the centuries, this city was forgotten, succumbing to the encroaching forest that concealed it from the outside world. The Spanish conquest led to the demise of the Inca empire, but Machu Picchu, due to its isolation, remained untouched and unknown to the conquerors. It was not until 1911 that Hiram Bingham, an American explorer, stumbled upon this hidden gem, and Machu Picchu resurfaced from the veil of time.
The Architectural Marvel
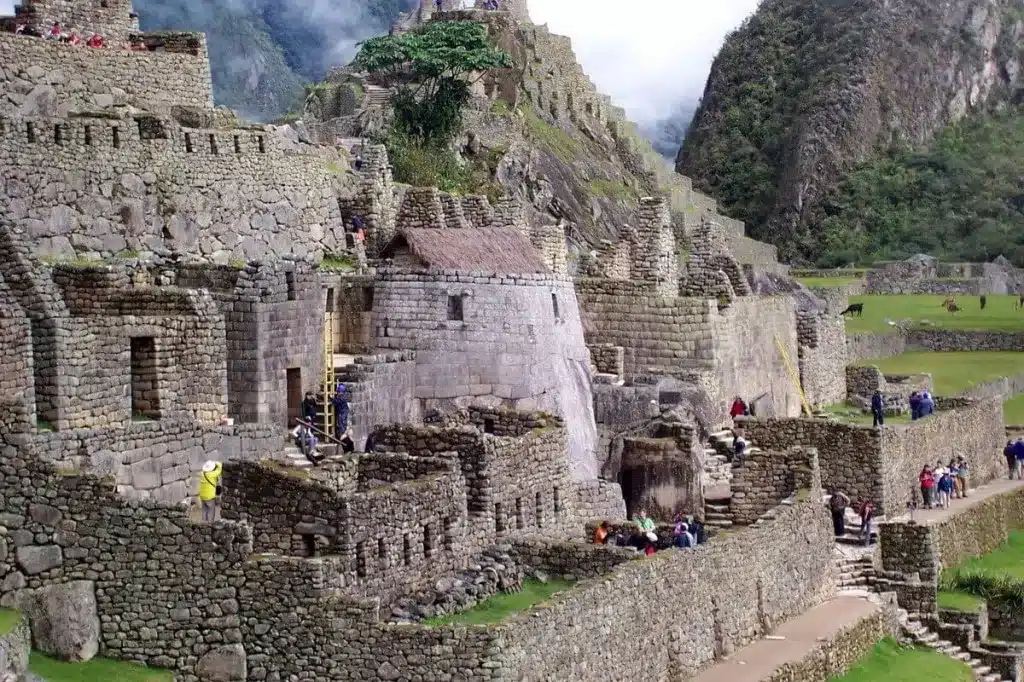

Machu Picchu’s awe-inspiring architecture reflects the Inca’s mastery of building and engineering. Constructed using a technique called ashlar, stones were cut to fit together without mortar, yet so precise that even a piece of paper would struggle to find its way between the stones. These structures have withstood both time and nature, resisting earthquakes that are common in this region.
The city is a marvel of Inca architecture, with certain structures of particular note. The Temple of the Sun, for instance, is a semi-circular structure built over a large granite rock. During the summer solstice, the sun shines through a window in the temple, illuminating a ceremonial stone inside. Similarly, the terraces seen all around were not just for farming but also for preventing landslides and erosion, exhibiting the Incas’ understanding of their environment.
The Astronomical Observatory

The Incas’ astronomical prowess is evident in the layout and construction of Machu Picchu. They observed the cosmos and its patterns, incorporating these into their city planning and architecture. This is particularly visible in the Intihuatana stone, which is often referred to as an astronomical clock or calendar.
The Intihuatana stone is precisely angled to point directly at the sun during the winter solstice. At exactly noon on the equinox days, the stone casts no shadow, demonstrating the Incas’ precision in their understanding of the sun’s movements. The astronomical knowledge of the Incas not only guided their farming activities but was deeply intertwined with their spiritual beliefs.
The Sacred Sites

Imbued with spiritual significance, Machu Picchu hosts a multitude of sacred sites. The Incas held a profound reverence for nature and its forces, a belief mirrored in their religious sites. Their spirituality was an integral part of their daily lives, and they often worshipped the sun, the moon, and the stars, which is evident in the design and architecture of Machu Picchu.
One such example is the Room of the Three Windows, an architectural masterpiece featuring trapezoidal windows that overlook the Sacred Plaza. The Condor Temple, another emblematic structure, has a rock formation resembling a condor in flight – a representation of the upper world in the Incan cosmology. These sites evoke the deeply spiritual nature of the Incas, providing glimpses into their complex belief systems.
Unraveling The Mystery of Its Purpose

The actual purpose of Machu Picchu remains shrouded in mystery. Some historians believe it to have been a royal estate for the Inca emperor Pachacuti, while others argue it to be a religious site, given its sacred constructions. This multifaceted city certainly held more than just one purpose, with areas dedicated to agriculture, residence, and worship.
Evidence supporting these theories varies. Traces of the Incan nobility, like ornamental artifacts and finely constructed buildings, support the royal estate theory. On the other hand, the presence of multiple temples and sacred spaces gives credence to the religious site theory. Regardless, the true purpose of this city may always be a subject of debate and speculation.
The Mystery of Its Abandonment
Just as its purpose, the reasons behind Machu Picchu’s abandonment remain obscure. Many theories abound, with the most accepted being the smallpox epidemic. It’s believed that the disease might have decimated the population, causing the survivors to abandon the city.
Some researchers suggest that the city was already in decline before the Spanish conquest, possibly due to internal conflicts or resource depletion. Yet, the lack of any Spanish artifacts or records about the city indicates that the Conquistadors never discovered Machu Picchu, leaving the reasons for its abandonment an enigma wrapped in the mists of time.
The Modern Discovery and Excavation

Hiram Bingham, a Yale professor, introduced Machu Picchu to the outside world in 1911. His expeditions, though intended to find the lost city of Vilcabamba, led to the rediscovery of this city concealed by thick vegetation. Bingham’s work sparked global interest in the Inca civilization and Machu Picchu.
Since its rediscovery, modern archaeology has played a significant role in decoding the mysteries of Machu Picchu. Through excavation and research, archaeologists have unveiled key insights about the Inca civilization, their lifestyle, beliefs, and the potential reasons for their sudden disappearance. Despite these strides, much about Machu Picchu remains a mystery, further tantalizing the world with its enigma.
Conservation Challenges and Future
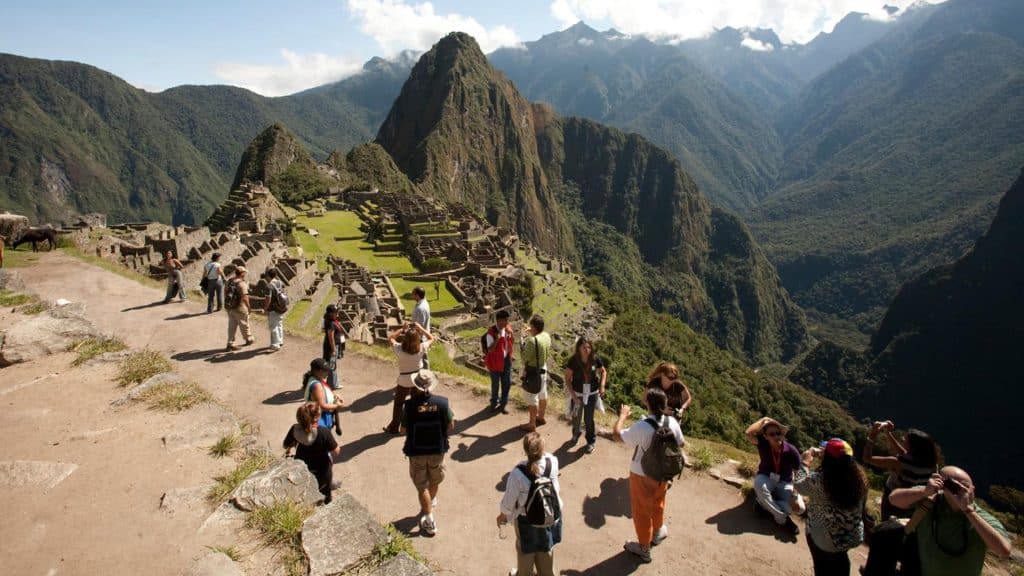

Today, the ancient city faces the challenges of modernity. Mass tourism, though a boost to Peru’s economy, threatens the preservation of this historical site. Machu Picchu, being situated in an earthquake-prone area, also risks structural damage from natural disasters.
To address these challenges, efforts are being undertaken by the Peruvian government and international organizations. Measures like limiting the number of visitors, promoting responsible tourism, and implementing structural reinforcements are being considered. These steps aim to protect and preserve Machu Picchu, ensuring that future generations can marvel at this testament to Inca ingenuity.
The Bottom Line
As we journey through the cloud-shrouded peaks of Machu Picchu, we explore not just stone and mortar but a civilization that holds a profound understanding of nature, the cosmos, and life. Machu Picchu, with its undeciphered secrets and unspoken tales, continues to beckon explorers, historians, and curious minds to its misty terraces. As one gazes upon the sacred city, one cannot help but wonder about the people who once roamed its paths, their dreams, their hopes, and the mysteries they left behind. The allure of Machu Picchu lies not just in its historical significance but also in the eternal enigma it presents – a testament to the timeless allure of the unknown.


